Register File
Ok great! We can perform our operations, but rather than just manually setting inputs and discarding outputs, how do we save them in memory?
The register file is the name for the construct holding data for each register. The number of registers, as well as their number of bits, can vary,
but Minecraft tends to work well with 8-bit registers in terms of compact builds.
We primarily will use 16, 8-bit registers (r0 … r15), which means we need four bits for a register file decoder (2^4 = 16).
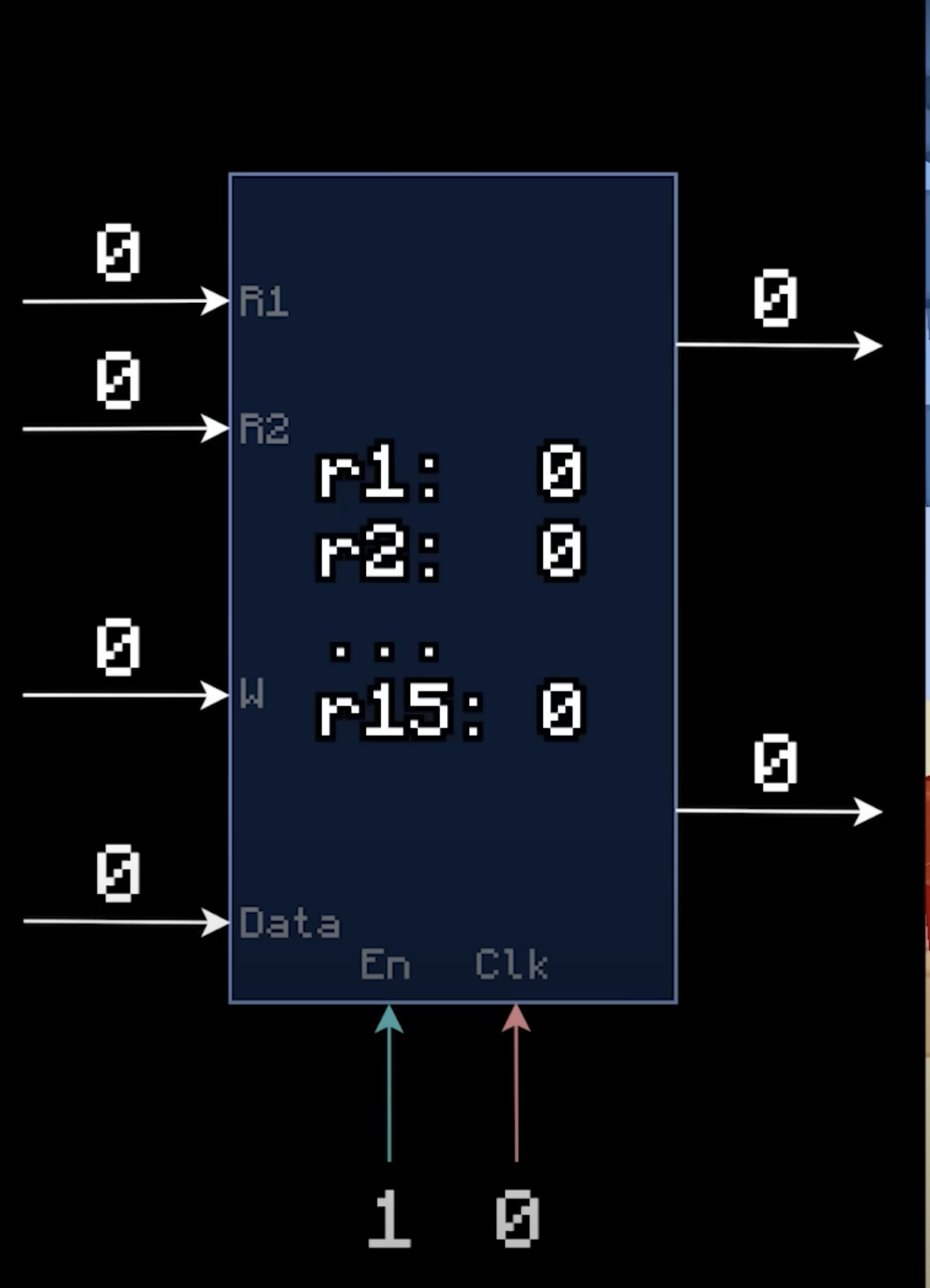
After you have read this entire module, the above diagram will start to make sense. It is essentially a dual-read register,
capable of reading two input registers,R0 and R1, along with a write register, W, and
some data to write to that write register. The outputs are reading those two registers. This visual is accredited to
matbatwings; it helps you understand conceptually how memory is stored.
Don't worry about the clock and enable input signals for now.
Disclaimer
Although this component is separate from all previous components, it is highly recommended that you know all prior architectural pieces before integrating your register file into your CPU.